- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
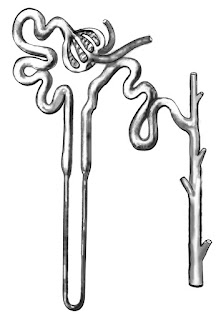 |
| Nephron |
The nephron is the minuscule auxiliary and practical unit of the kidney. It is made out of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.
The renal corpuscle comprises of a tuft of vessels called a glomerulus and an enveloping Bowman's case.
The renal tubule reaches out from the container. The container and tubule are associated and are made out of epithelial cells with a lumen.
Contrast induced neuropathy
A solid grown-up has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in every kidney. Blood is sifted as it goes through three layers:
the endothelial cells of the hairlike divider, its storm cellar film, and between the foot cycles of the podocytes of the coating of the container.
The tubule has contiguous peritubular vessels that run between the diving and rising segments of the tubule.
Nursing diagnosis for Chronic Kidney Disease
As the liquid from the container streams down into the tubule, it is handled by the epithelial cells coating the tubule:
water is reabsorbed and substances are traded; first with the interstitial liquid external the tubules, and afterward into the plasma in the nearby peritubular vessels through the endothelial cells covering that slim.
This cycle controls the volume of body liquid just as levels of many-body substances. Toward the finish of the tubule, the staying liquid—pee—exits: it is made out of the water, metabolic waste, and poisons.
The inside of Bowman's container, called Bowman's space, gathers the filtrate from the sifting vessels of the glomerular tuft, which likewise contains mesangial cells supporting these vessels.
These segments work as the filtration unit and make up the renal corpuscle. The separating structure has three layers made out of endothelial cells, a storm cellar film, and podocytes.
The tubule has five anatomically and practically various parts:
the proximal tubule, which has a tangled area the proximal tangled tubule followed by a straight segment; the circle of Henle, which has two sections, the diving circle of Henle and the rising circle of Henle; the distal tangled tubule; the associating tubule, and the last piece of nephron the gathering channels.
Nephrons have two lengths with various pee concentrating limits: long juxtamedullary nephrons and short cortical nephrons.
Structure
A nephron is a useful unit of the kidney. This implies that each different nephron is the place the principle work of the kidney is performed.
A nephron is made of two sections:
a renal corpuscle, which is the underlying sifting segment, and
a renal tubule that cycles and diverts the sifted liquid.
Renal corpuscle
The renal corpuscle is the site of the filtration of blood plasma. The renal corpuscle comprises of the glomerulus, and the glomerular case or Bowman's case.
Bowman's case
The Bowman's case additionally called the glomerular container, encompasses the glomerulus. It is made out of an instinctive internal layer shaped by specific cells called podocytes, and a parietal external layer made out of the basic squamous epithelium.
The four components used to make and deal with the filtrate are filtration, reabsorption, discharge, and discharge.
Filtration happens in the glomerulus and is generally uninvolved: it is subject to the intracapillary circulatory strain.
Around one-fifth of the plasma is sifted as the blood goes through the glomerular vessels; four-fifths proceeds into the peritubular vessels.
Ordinarily, the main parts of the blood that are not sifted into Bowman's container are blood proteins, red platelets, white platelets, and platelets.
More than 150 liters of liquid enter the glomeruli of a grown-up each day: 99% of the water in that filtrate is reabsorbed.
Reabsorption happens in the renal tubules and is either detached, because of dissemination, or dynamic, due to siphoning against a fixation inclination.
The discharge additionally happens in the tubules and is dynamic. Substances reabsorbed include water, sodium chloride, glucose, amino acids, lactate, magnesium, calcium phosphate, uric corrosive, and bicarbonate.
Substances emitted incorporate urea, creatinine, potassium, hydrogen, and uric corrosive. A portion of the hormones which signal the tubules to change the reabsorption or discharge rate, and accordingly look after homeostasis, incorporate antidiuretic hormone, aldosterone, parathyroid hormone, atrial natriuretic peptide, and cerebrum natriuretic peptide.
A countercurrent framework in the renal medulla gives the system to creating a hypertonic interstitium, which permits the recuperation of without solute water from inside the nephron and returning it to the venous vasculature when fitting.
A few illnesses of the nephron prevalently influence either the glomeruli or the tubules. Glomerular ailments incorporate diabetic nephropathy, glomerulonephritis, and IgA nephropathy; renal rounded sicknesses incorporate intense cylindrical putrefaction and polycystic kidney malady.
A few illnesses of the nephron prevalently influence either the glomeruli or the tubules. Glomerular ailments incorporate diabetic nephropathy, glomerulonephritis, and IgA nephropathy; renal rounded sicknesses incorporate intense cylindrical putrefaction and polycystic kidney malady.
EGFR CALCULATION
Structure
A nephron is a useful unit of the kidney. This implies that each different nephron is the place the principle work of the kidney is performed.
A nephron is made of two sections:
a renal corpuscle, which is the underlying sifting segment, and
a renal tubule that cycles and diverts the sifted liquid.
Glomerular filtration rate
Renal corpuscle
The renal corpuscle is the site of the filtration of blood plasma. The renal corpuscle comprises of the glomerulus, and the glomerular case or Bowman's case.
The arterioles from the renal dissemination enter and leave the glomerulus at the vascular post. The glomerular filtrate leaves the Bowman's case at the renal tubule at the urinary shaft.
Glomerulus
The glomerulus is the organization known as a tuft, of sifting vessels situated at the vascular shaft of the renal corpuscle in Bowman's container.
The glomerulus is the organization known as a tuft, of sifting vessels situated at the vascular shaft of the renal corpuscle in Bowman's container.
Every glomerulus gets its blood flexibly from an afferent arteriole of the renal course. The glomerular circulatory strain gives the main thrust to water and solutes to be sifted through of the blood plasma, and into the inside of Bowman's case, called Bowman's space.
Just about a fifth of the plasma is sifted in the glomerulus. The rest passes into an efferent arteriole.
Just about a fifth of the plasma is sifted in the glomerulus. The rest passes into an efferent arteriole.
The width of the efferent arteriole is more modest than that of the afferent, and this distinction builds the hydrostatic weight in the glomerulus.
Dialysis side effects
Bowman's case
The Bowman's case additionally called the glomerular container, encompasses the glomerulus. It is made out of an instinctive internal layer shaped by specific cells called podocytes, and a parietal external layer made out of the basic squamous epithelium.
Liquids from blood in the glomerulus are ultrafiltered through a few layers, bringing about what is known as the filtrate.
The filtrate next moves to the renal tubule, where it is additionally handled to shape pee. The various phases of this liquid are on the whole known as the rounded liquid.
Renal tubule
The renal tubule is the bit of the nephron containing the cylindrical liquid sifted through the glomerulus. Subsequent to going through the renal tubule, the filtrate proceeds to the gathering channel framework.
The segments of the renal tubule are:
Proximal tangled tubule
Circle of Henle
Diving appendage of the circle of Henle
Climbing appendage of the circle of Henle
The rising appendage of the circle of Henle is partitioned into 2 fragments:
The filtrate next moves to the renal tubule, where it is additionally handled to shape pee. The various phases of this liquid are on the whole known as the rounded liquid.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF KIDNEY PROBLEM?
Renal tubule
The renal tubule is the bit of the nephron containing the cylindrical liquid sifted through the glomerulus. Subsequent to going through the renal tubule, the filtrate proceeds to the gathering channel framework.
The segments of the renal tubule are:
Proximal tangled tubule
Circle of Henle
Diving appendage of the circle of Henle
Climbing appendage of the circle of Henle
The rising appendage of the circle of Henle is partitioned into 2 fragments:
The lower end of the climbing appendage is exceptionally slender and is lined by basic squamous epithelium. The distal bit of rising appendage is thick and is lined by straightforward cuboidal epithelium.
Slight rising appendage of the circle of Henle
Thick climbing appendage of the circle of Henle
Distal tangled tubule
Associating tubule
Blood from the efferent arteriole, containing all that was not sifted through in the glomerulus, moves into the peritubular vessels, small veins that encompass the circle of Henle and the proximal and distal tubules, where the cylindrical liquid streams. Substances at that point reabsorb from the last back to the circulation system.
The peritubular vessels at that point recombine to shape an efferent venule, which joins with efferent venules from different nephrons into the renal vein and rejoins the principle circulatory system.
Length contrast
Cortical nephrons start high in the cortex and have a short circle of Henle which doesn't infiltrate profoundly into the medulla. Cortical nephrons can be partitioned into shallow cortical nephrons and mid cortical nephrons.
Juxtamedullary nephrons start low in the cortex close to the medulla and have a long circle of Henle which enters profoundly into the renal medulla:
Slight rising appendage of the circle of Henle
Thick climbing appendage of the circle of Henle
Distal tangled tubule
Associating tubule
Blood from the efferent arteriole, containing all that was not sifted through in the glomerulus, moves into the peritubular vessels, small veins that encompass the circle of Henle and the proximal and distal tubules, where the cylindrical liquid streams. Substances at that point reabsorb from the last back to the circulation system.
The peritubular vessels at that point recombine to shape an efferent venule, which joins with efferent venules from different nephrons into the renal vein and rejoins the principle circulatory system.
Length contrast
Cortical nephrons start high in the cortex and have a short circle of Henle which doesn't infiltrate profoundly into the medulla. Cortical nephrons can be partitioned into shallow cortical nephrons and mid cortical nephrons.
Juxtamedullary nephrons start low in the cortex close to the medulla and have a long circle of Henle which enters profoundly into the renal medulla:
just they have their circle of Henle encompassed by the vasa recta. These long circles of Henle and their related vasa recta make a hyperosmolar inclination that takes into account the age of concentrated pee.
Likewise, the barrette twist infiltrates up to the inward zone of the medulla.
Juxtamedullary nephrons are discovered distinctly in winged animals and warm-blooded creatures, and have a particular area:
Juxtamedullary nephrons are discovered distinctly in winged animals and warm-blooded creatures, and have a particular area:
medullary alludes to the renal medulla, while juxta alludes to the overall situation of the renal corpuscle of this nephron - close to the medulla, yet in the cortex.
At the end of the day, a juxtamedullary nephron is a nephron whose renal corpuscle is close to the medulla, and whose proximal tangled tubule and its related circle of Henle happen further in the medulla than the other sort of nephron, the cortical nephron.
The juxtamedullary nephrons contain just about 15% of the nephrons in the human kidney. The liquid in the filtrate entering the proximal tangled tubule is reabsorbed into the peritubular vessels, including the greater part of the sifted salt and water and all separated natural solutes.
Circle of Henle
The circle of Henle is a U-formed cylinder that stretches out from the proximal tubule. It comprises of a plummeting appendage and a climbing appendage.
The juxtamedullary nephrons contain just about 15% of the nephrons in the human kidney. The liquid in the filtrate entering the proximal tangled tubule is reabsorbed into the peritubular vessels, including the greater part of the sifted salt and water and all separated natural solutes.
Circle of Henle
The circle of Henle is a U-formed cylinder that stretches out from the proximal tubule. It comprises of a plummeting appendage and a climbing appendage.
It starts in the cortex, getting filtrate from the proximal tangled tubule, stretches out into the medulla as the plummeting appendage, and afterward re-visitations of the cortex as the rising appendage to discharge into the distal tangled tubule.
The essential function of the circle of Henle is to empower a creature to deliver concentrated pee, not by expanding the rounded focus, but rather by delivering the interstitial liquid hypertonic.
In spite of the fact that the gathering conduit is typically impermeable to water, it gets porous within the sight of the antidiuretic hormone.
In spite of the fact that the gathering conduit is typically impermeable to water, it gets porous within the sight of the antidiuretic hormone.
ADH influences the capacity of aquaporins, bringing about the reabsorption of water atoms as it goes through the gathering conduit.
Aquaporins are film proteins that specifically direct water atoms while forestalling the entry of particles and different solutes.
As much as 75% of the water from pee can be reabsorbed as it leaves the gathering channel without really trying. In this way the degrees of ADH decide if pee will be focused or weakened.
An expansion in ADH means that lack of hydration, while water adequacy brings about a reduction in ADH taking into account weakened pee.
Lower segments of the gathering organ are likewise penetrable to urea, permitting some of it to enter the medulla, hence keeping up its high fixation.
Juxtaglomerular mechanical assembly
The juxtaglomerular mechanical assembly is a specific locale related to the nephron, however separate from it.
Lower segments of the gathering organ are likewise penetrable to urea, permitting some of it to enter the medulla, hence keeping up its high fixation.
Juxtaglomerular mechanical assembly
The juxtaglomerular mechanical assembly is a specific locale related to the nephron, however separate from it.
It delivers and secretes into the flow the chemical renin, which severs angiotensinogen and brings about the ten amino corrosive substance angiotensin-1. A-1 is then changed over to angiotensin-2, a strong vasoconstrictor, by eliminating two amino acids:
this is refined by angiotensin changing over catalyst. This grouping of functions is alluded to as the renin-angiotensin framework or renin-angiotensin-aldosterone framework.
The JGA is situated between the thick rising appendage and the afferent arteriole. It contains three parts: the macula densa, juxtaglomerular cells, and extraglomerular mesangial cells.
Clinical essentialness
Ailments of the nephron prevalently influence either the glomeruli or the tubules. Glomerular infections incorporate diabetic nephropathy, glomerulonephritis, and IgA nephropathy; renal rounded ailments incorporate intense cylindrical putrefaction, renal rounded acidosis, and polycystic kidney malady.
Ailments of the nephron prevalently influence either the glomeruli or the tubules. Glomerular infections incorporate diabetic nephropathy, glomerulonephritis, and IgA nephropathy; renal rounded ailments incorporate intense cylindrical putrefaction, renal rounded acidosis, and polycystic kidney malady.